Augmented reality is the integration of digital information with the user’s environment in real time.
How does it work?
AR, is a technology enriching the real world with digital information and media, such as 3D models and videos, overlaying in real-time the camera view of your smartphone, tablet, PC or connected glasses.
The technology functions by enhancing one’s current perception of reality. There are many different applications in which AR can be used:
- Archaeology Architecture Construction
- Art Commerce Education
- Emergency management Everyday Gaming
- Search and Rescue Medical Beauty
- Industrial design Military Navigation
- Spatial immersion Office workplace Task Support
- Sports + Entertainment TV Tourism
- Interaction Translation etc
There has been a recent boom in the Augmented Reality industry, with many of the large multinational companies, e.g. Google and Microsoft, racing to create the best AR product, that will be available to the public. There are already some 1st generation products that are already in the market today, such as:
Google Glass (2013)![]()
It is an optical head-mounted display, that is designed in the shape of a pair of reading glasses. It was developed with the idea to produce a ubiquitous computer.
The headset displays information through a projection  from a prism attached to the right corner of the
from a prism attached to the right corner of the
frame. The idea behind it was meant to be a hands-free format. When communicating with Glass, simple voice commands would react through connecting the headset to the internet.
A prototype for the product was released called “Glass Explorers” in the US in 2013 for  $1,500, and then became available to the public in 2014 for the same price. The product failed to take off, as it received a lot of criticism and legislative action was taken against it due to privacy and safety concerns. The public were also hesitant to spend $1,500 on a 1st generation product that had not been seen on the market anywhere else at the time.
$1,500, and then became available to the public in 2014 for the same price. The product failed to take off, as it received a lot of criticism and legislative action was taken against it due to privacy and safety concerns. The public were also hesitant to spend $1,500 on a 1st generation product that had not been seen on the market anywhere else at the time.
The Google Glass AR headset is no longer on sale, but Google says they have put it back in the development stage.
IKEA AR furniure APP (2013)

Also in 2013, IKEA launched their new catalogue, allowing customers to place 3-D versions of furniture in their homes, as seen above. ‘The physical catalogue acts as an anchor for the virtual furniture and a way to gauge the correct scale for the products shown on screen.‘ – WIRED
How it works:
Customers look through the physical catalogue. When they decide upon the piece of furniture, they look for a plus symbol on the page and hover their phone or tablet over it until and screen appears. This then asks to scan the images on the page. At this stage they will have the option to place their chosen piece of furniture in their chosen environment, or see a 360-degree view of a room, additional product information and videos.
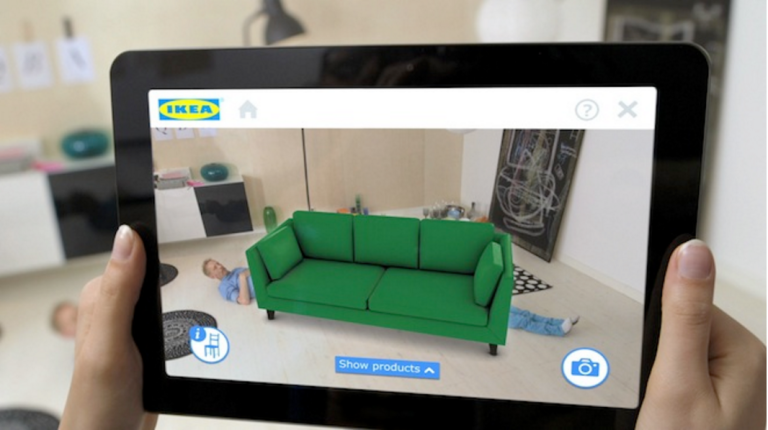
When the app first came out in 2013, there were only 100 pieces of furniture available to show, compared to the 300+ items in the catalogue. That now being 3 years ago, there is more products to view and options available, such as colour etc. When the piece of furniture been chosen, the customer simply places their catalogue in the desire spot and the IKEA furniture will appear.
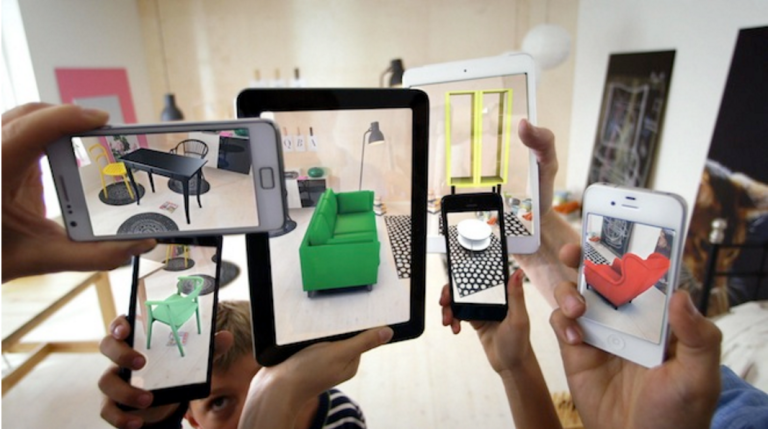

Mattias Jöngard, Ikea’s Global Communication Integration Manager, said: “The technology or the functions themselves are not are not really the driving force. Rather, it’s how can it add value to our consumers?”
‘Ikea did a little digging into their customers’ habits and found that around 14 percent of people have bought a wrong-sized piece of furniture and more than 70 percent of people don’t know how big their homes really are.
The app’s other features, in particular, the time-lapse images allow you to watch a room being decorated piece-by-piece, is a great way to get some inspiration on how to do up your own home. Which, Sjöberg says, is the whole point. “I think this application should always try to enrich the catalog and enrich the experience for consumers—and that is an ongoing journey.”’ – WIRED
References:
http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/augmented-reality-AR
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Glass
